

Su `y' if nodrug_b=0 & nodrug_a=0 & e(sample)=1 Local indvar prosociality intrinsic combined_motivation income pracdoc maleĮststo, title("`y'"): reghdfe `y' nodrug_b nodrug_a if levelcode=2, vce(robust) absorb(diseasecode clinicid) Global treatment = "corrtreat pcorrtreat corrdrug pcorrdrug referral" However, I am unable to create a nested loop that allows this. Matrix initialization is better done using the sample function chained directly as the first argument of the matrix function, as shown in the following snippet.I want to interact each term in the local "indvar" with the variables "nodrug_b" "nodrug_a" in separate regressions. Mat1 <- sample(1:100, 1, replace=TRUE)Īlthough, the nested loop structure works fine in the previous example code. For Loop For loops are controlled by a looping vector. The break function is used to break out of loops, and next halts the processing of the current iteration and advances the looping index. nrow and ncol return the number of rows or columns of the array, respectively. The most commonly used loop structures in R are for, while and apply loops. Note that the general notation is the same as the previous example, except that the end of the range is calculated with the nrow and ncol functions. This can be utilized to iterate over matrix elements and initialize them with random values.

For example, // creating float type variables float num1 3.0f float num2 3.5f float num3 3E-5f // 3x10-5 // creating double type variables double num4 3.0 double num5 3. Floating-point numbers are used for decimal and exponential values. Nested loops can be implemented using the for loop structure. In C++, both float and double data types are used for floating-point values. Use Nested for Loop to Iterate Over Matrix Elements in R Before you start the loop, you must always allocate.
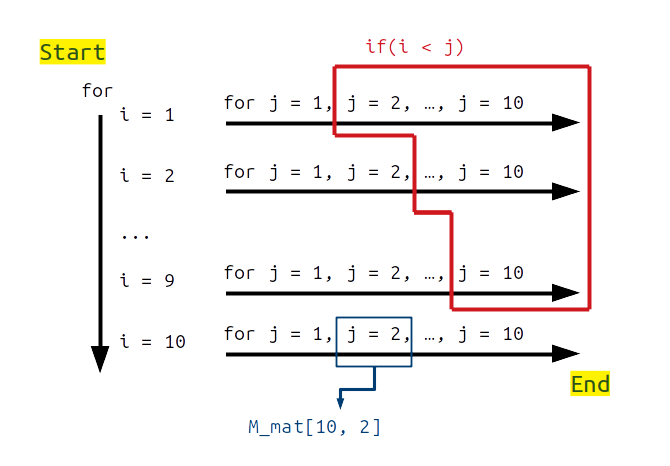
#Double loop in r code#
The following example code creates a string vector copied to another vector of the same size using the for loop. Every for loop has three components: The output: output <- vector(double, length(x)). Note that 1: notation is important, and it specifies the beginning of the range. In this case, the length function is utilized to calculate the size of the vec1 vector and iterate from the first element to the end. Remember that control flow commands are the commands that enable a program to branch between alternatives, or to take decisions, so to speak. We can also implement the for loop, where the index is exposed as a variable. According to the R base manual, among the control flow commands, the loop constructs are for, while and repeat, with the additional clauses break and next. vec1 <- c("ace", "spades", "king", "spades", "queen", "spades", "jack", About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators. The for loop doesn’t return output, so we need to call the print function to output the word value on each iteration. RIF Store Silv-r Tone 2021 model Double Loop Bangle Saint Sta Bracelet with RIF,Store,Loop,with,Sta,Bracelet,Clothing, Shoes Jewelry. Item is an object that stores the iterated element from the set. It repeats the given code block multiple times. The for loop is available in R language with similar heuristics as in most programming languages. This article will introduce the nested for loops in R.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
